Motivation
This procedure describes the setup of communication between S7-1200/1500 devices in a network to exchange data.
Instructions
Device and network configuration
-
Open the device configuration (“Devices & networks”) and switch to the network view.
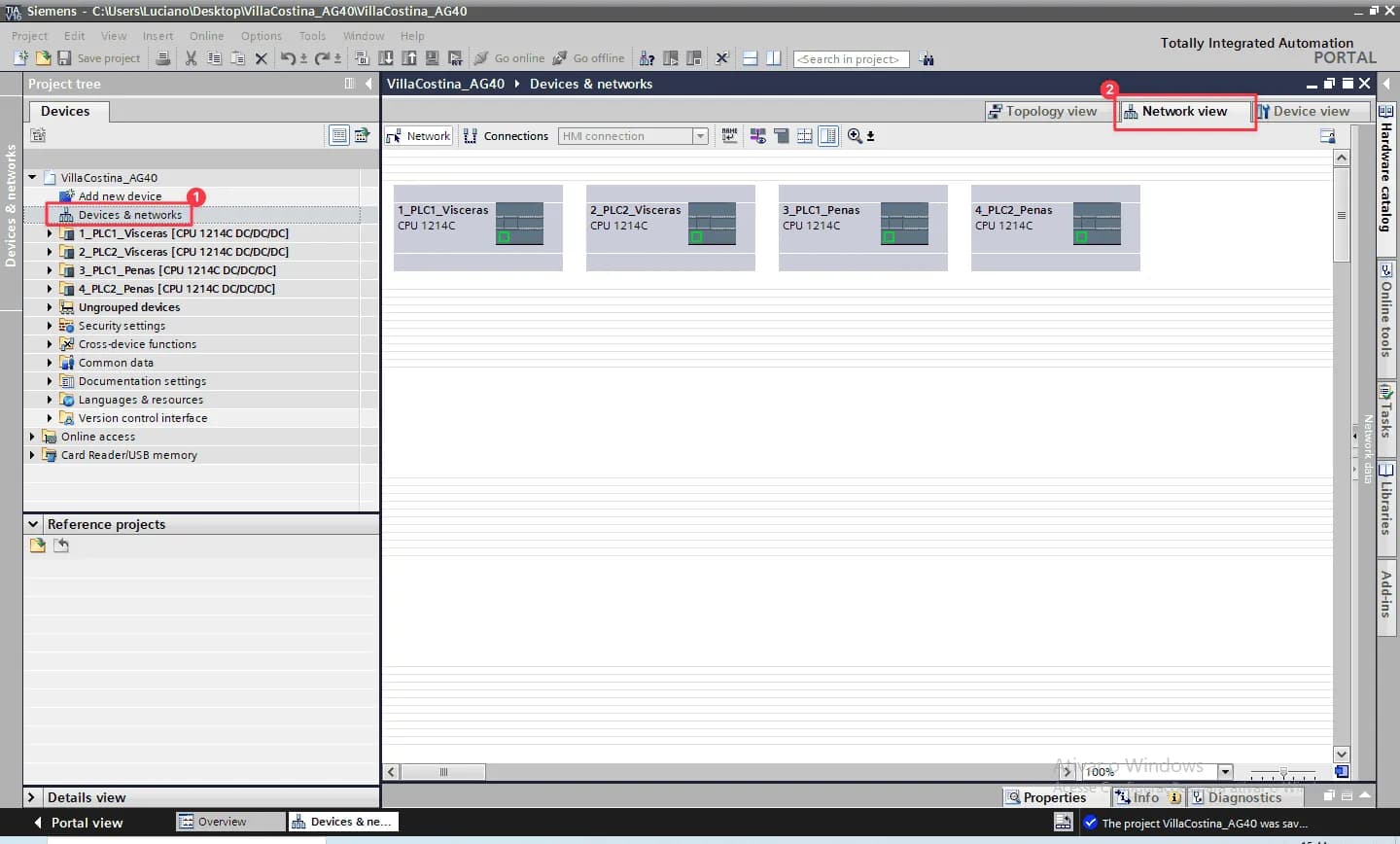
-
Right-click on the interface of a CPU and select “Add subnet” from the context menu.
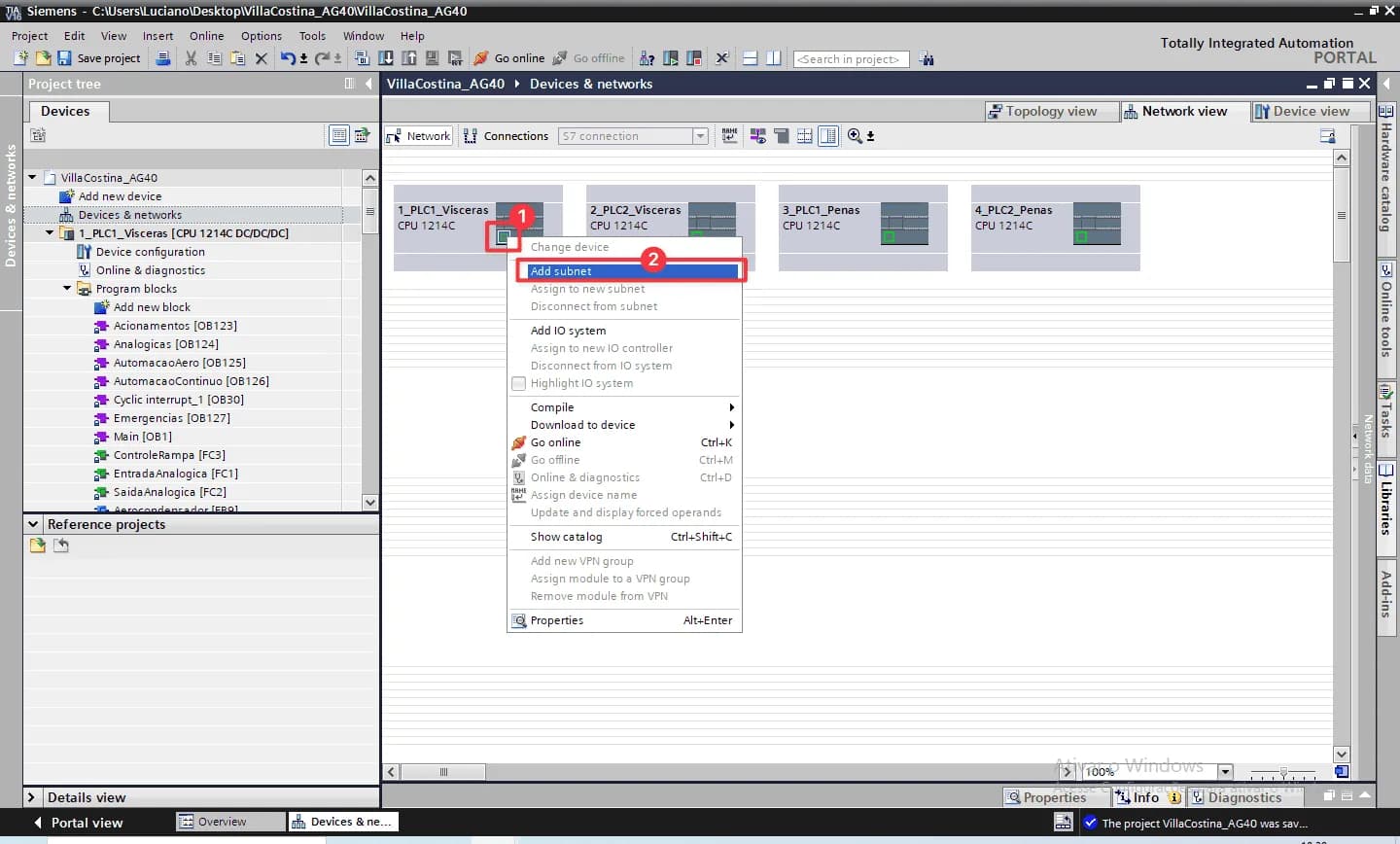
-
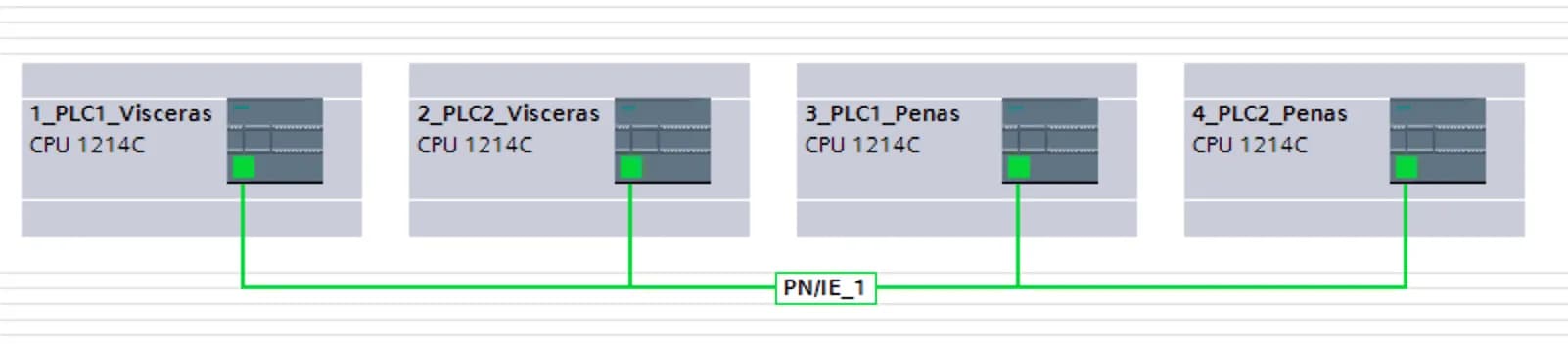
Connect each device to the subnet by dragging from the device interface to the subnet or vice versa - simply click and hold on one interface, drag the mouse to the target, and release to establish the connection.
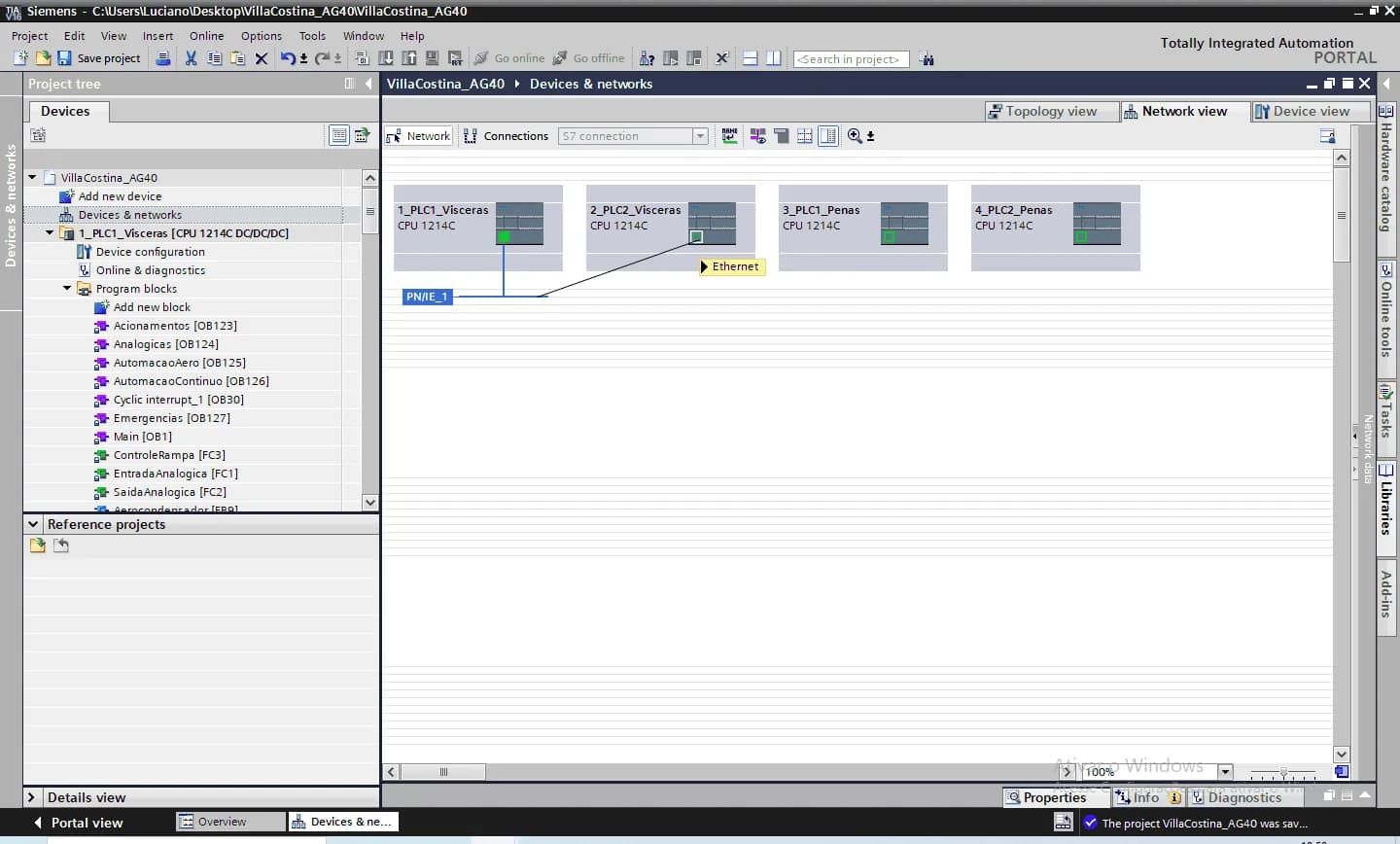
As an alternative, you can skip the “Add subnet” step and connect all devices simply by dragging the mouse from one interface to another.
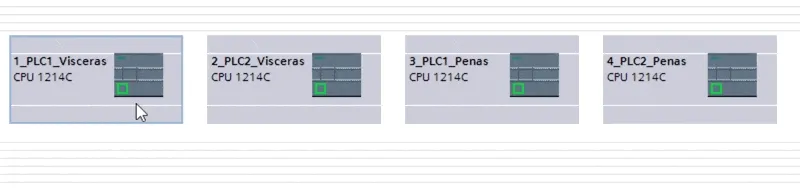
Resulting connections should look like this:
-
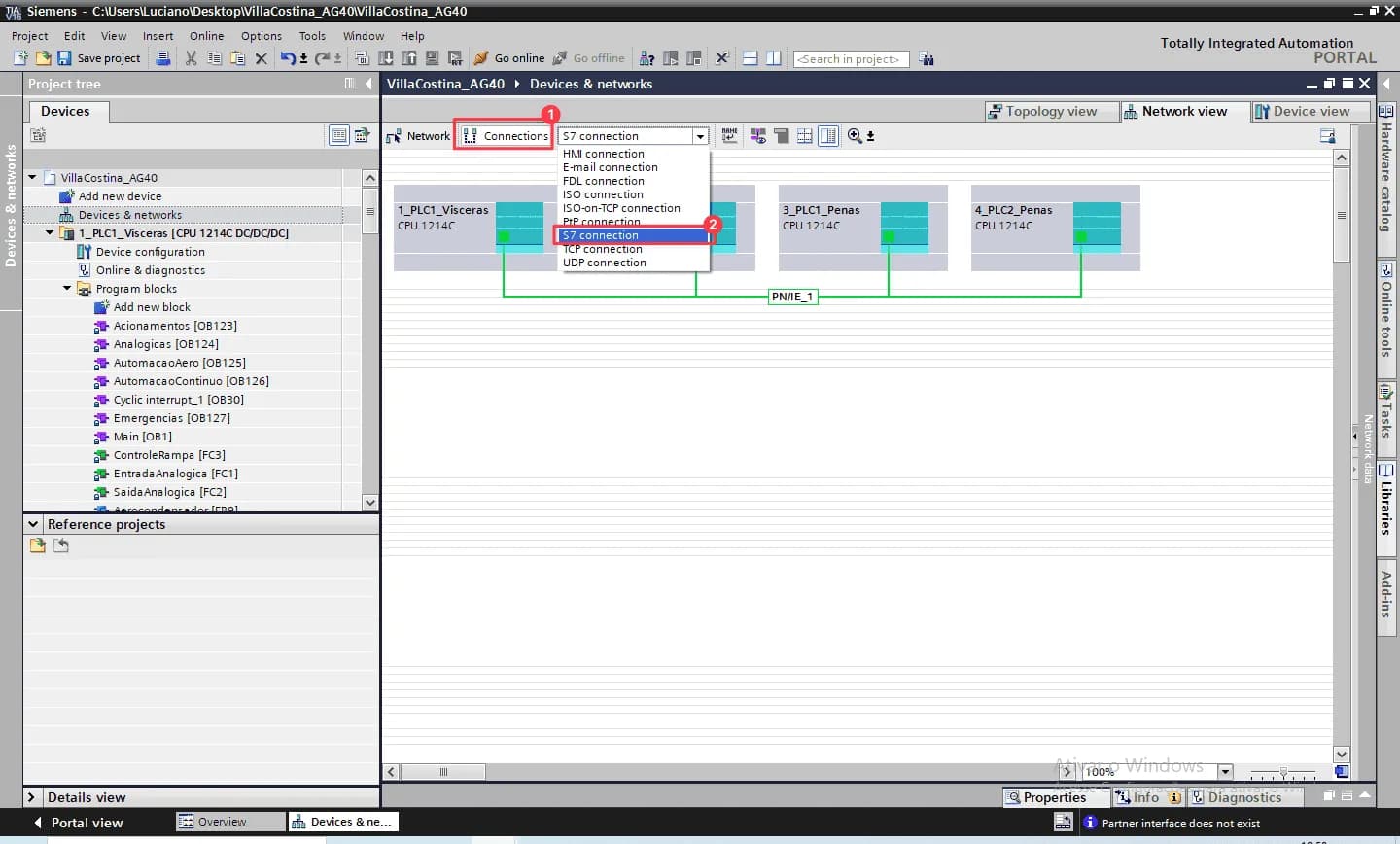
Now click “Connections” and choose “S7 connection”.
-
Right-click on each CPU and select “Add new connection” from the context menu.
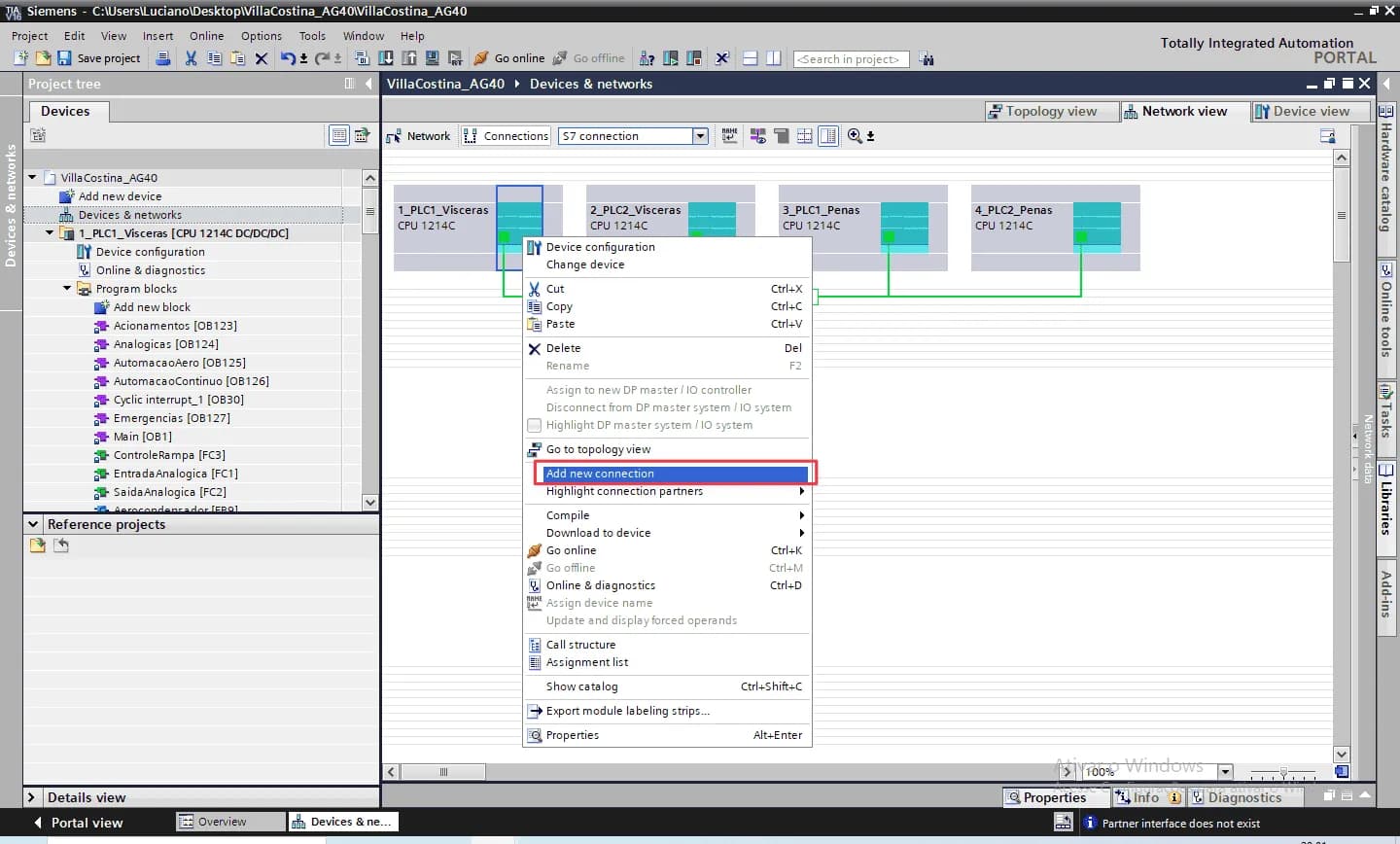
Alternatively, connections can also be established by dragging the mouse from one CPU interface to another in this view.
-
In the “Add new connection” dialog, first ensure that “S7 connection” type is selected. Then select the target CPU, make sure the right “Local ID” is configured and then click “Add” to add the connection. Repeat for all connections to be established.
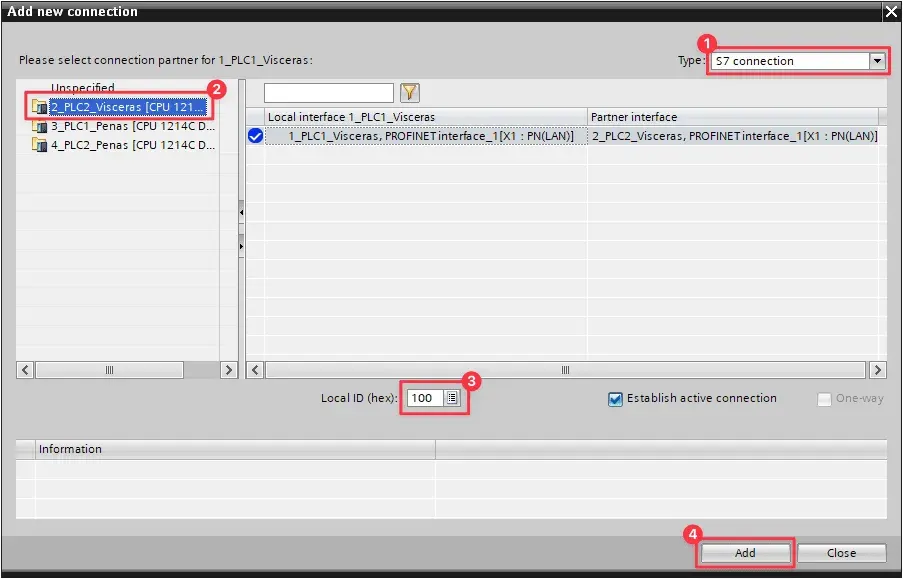
Each connection has a “Local ID” that must be unique for the CPU. As recommended practice, use a sequence starting at
100(ex.:100,101,102, …). -
In the “Network view”, select the “Connections” tab to show the connection table. Rename each local connection name to correspond to the connection (ex.:
S7_Connection_PLC1_PLC2).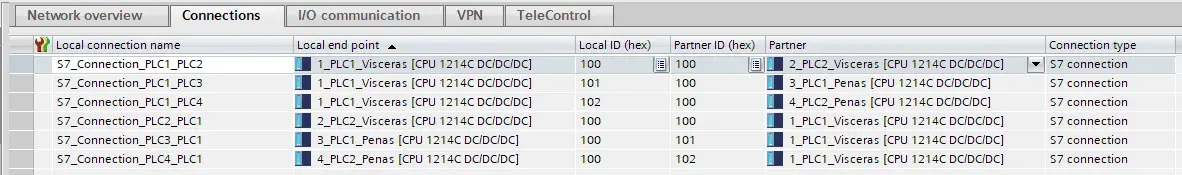
Note that for each connection created from source CPU to target CPU, a counterpart connection is automatically created. This is not strictly necessary for communication via PUT/GET instructions, since we could establish “one-way” connections by selecting an “Unspecified” device and manually configuring the connection. This approach could be used if limited connection resources are a concern. However, for easier configuration and “self-documentation” in TIA Portal network view, it is recommended to configure “two-way” connections.
-
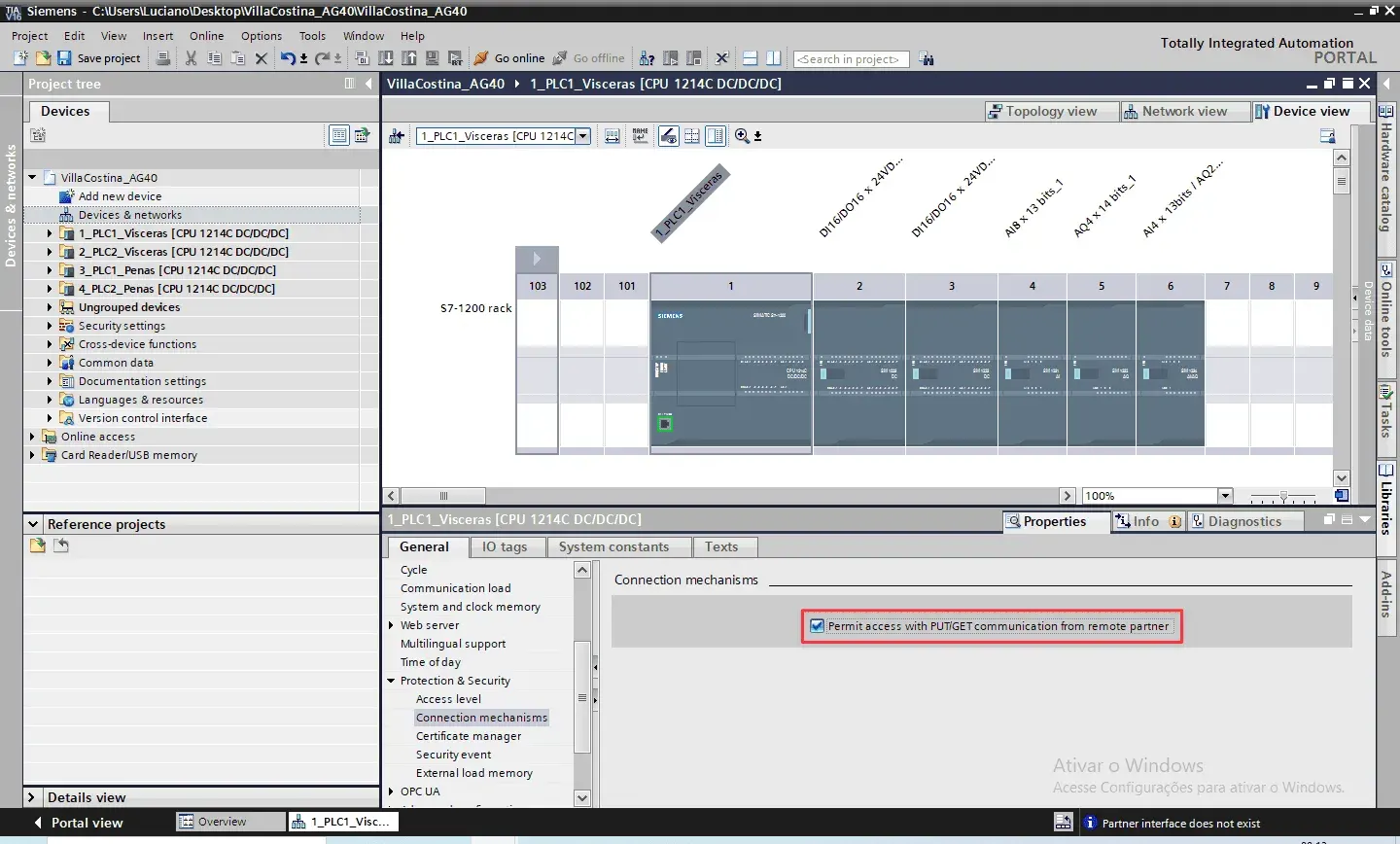
For each device, open the properties of the CPU and navigate to “Protection & Security > Connection mechanisms”. Activate the function “Permit access with “PUT/GET communication from remote partner”.
Program
Reference project: Villa Costina v1.3.0 (2025-10-15). This project provides a template for interchange of information among 4 S7-1200 CPUs.
typeS7ConnectionControl PLC data type
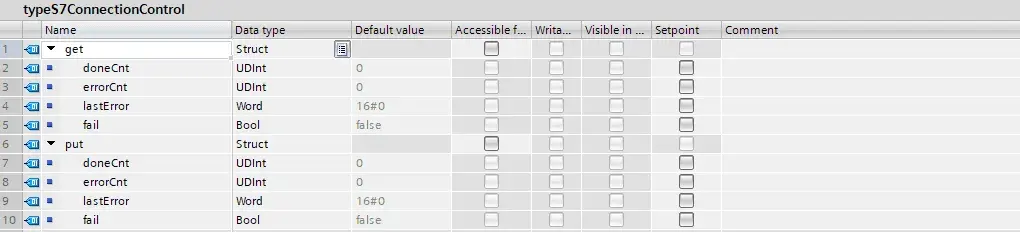
This PLC data type is present in the client CPU program (PLC1) and contains control information for PUT/GET instructions.
S7Connections/S7ConnectionsData DB
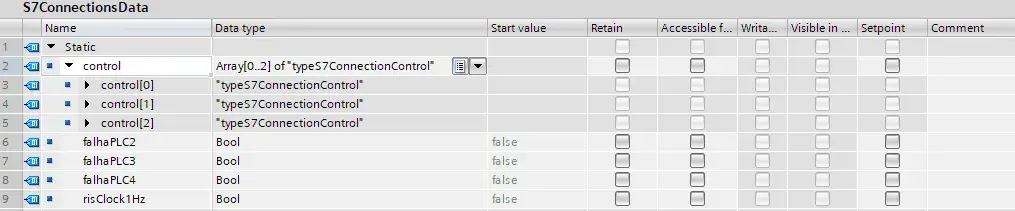
This data block is present in the client CPU (PLC1) contains control data for PUT/GET instructions.
S7Connections/Send_PLCx and S7Connections/Receive_PLCx DBs
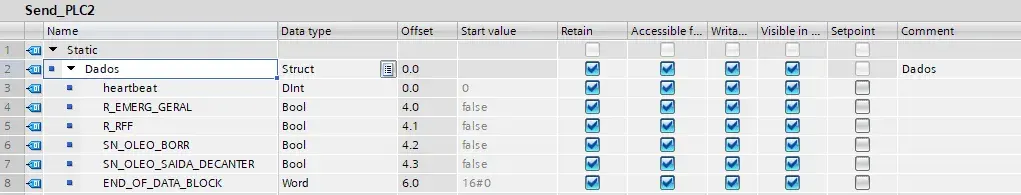
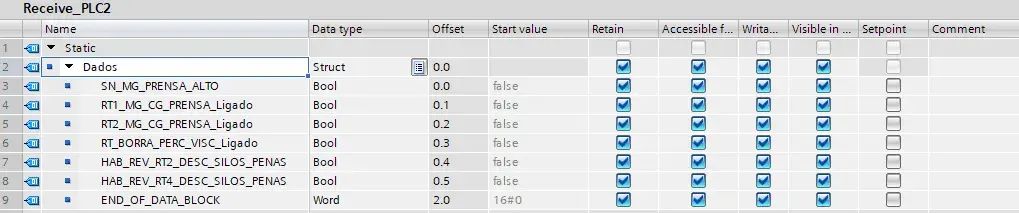
These data blocks are present in the client CPU (PLC1) and also with counterparts in the server CPUs (PLC2, PLC3 and PLC4). They contain the data do be transferred between CPUs.
Notes:
- “Retain” is selected in the elements of these blocks, but it is actually not required and probably wrongly configured in this application.
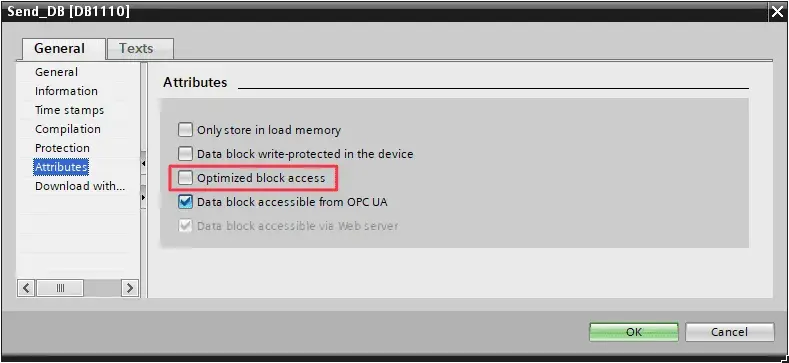
- In block properties, under “Attributes” tab, you must uncheck the “Optimized block access” option.
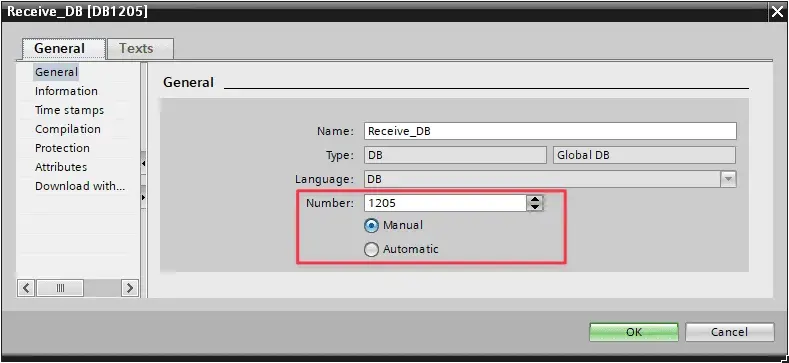
- In block properties of the server PLCs (PLC2, PLC3 and PLC4), under “General” tab, you should set DB number to “Manual”.
S7Connections FB
This function block implements and coordinates the calls to PUT/GET instructions.
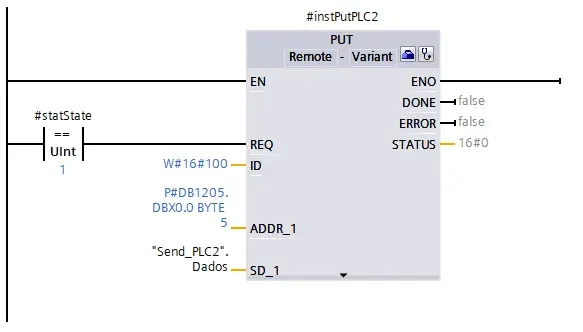
In the PUT/GET instruction call, pay attention to these parameters:
IDmust be correctly configured to the “Local ID” of the S7 corresponding connection.ADDR_1is a pointer to the area on the partner CPU, containing also the data type and the number of elements transferred.SD_1is a pointers to the area on the local CPU.
Note: Along with the normal data, a heartbeat is transferred to the partner CPU in the form of a
DINTvariable incrementing at each second, so that the partner can detect a failure in communication.
The S7Connections FB is called in the Main OB.
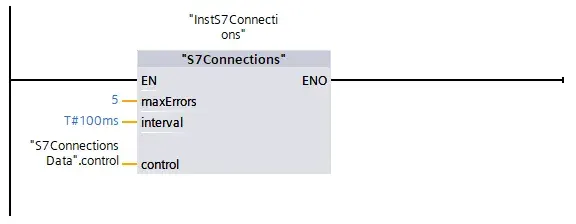
The "S7ConnectionsData".falhaPLCx tags should be used to signal communication error in SCADA/HMI and also take safety action on outputs that depend on data from partner CPUs.
Communication failure detection in server CPUs
Heartbeat signal must be used in the server CPUs to detect communication failure and take safety actions on outputs that depend on data from client CPU.
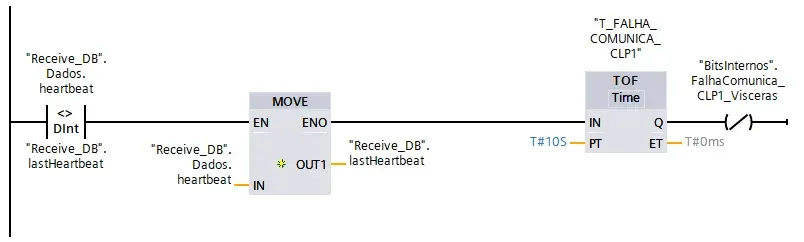
Note about inter-CPU communication
PUT/GET communication
This is the modern, simplified approach for S7-1200:
Advantages:
- Much simpler implementation - single instruction does it all
- Automatic connection management - no need for TCON/TDISCON
- Less programming overhead - fewer blocks and less code
- Unilateral communication - one CPU can read/write to another without the partner needing special programming
- Integrated diagnostics - status information built into the instruction
How it works:
- One CPU acts as the client, initiating PUT (write) or GET (read) operations
- The partner CPU just needs to allow the connection in its protection settings
- Connection is established automatically when needed
- Data is transferred directly to/from specified data blocks
Typical use:
- Reading process values from another CPU
- Writing setpoints or commands to a partner CPU
- Simple master-slave architectures
TCON/TDISCON/TSEND/TRCV (ISO-on-TCP)
This is the older, more traditional method:
Characteristics:
- Explicit connection management - you manually establish (TCON) and disconnect (TDISCON)
- Separate send/receive operations - TSEND and TRCV (not TREC) handle data transfer
- More complex programming - requires state machines and connection monitoring
- Bidirectional - typically both sides need programming for send/receive
Modern recommendation
For new projects, Siemens recommends PUT/GET because:
- It’s specifically optimized for S7-1200/1500 communication
- Significantly reduces programming effort
- Built-in safety through S7 protocol security
- Easier troubleshooting and maintenance
The “safety” in modern implementations comes from the S7 protocol itself (authentication, connection monitoring) rather than from manual connection management. PUT/GET isn’t less safe - it just handles the complexity internally.
References
- How you configure a connection in the TIA Portal?, Entry type: FAQ Entry ID: 109486139, Entry date: 2023-07-17
- With which devices can the S7-1200 communicate via the integrated PROFINET interface and which protocols does the S7-1200 support?, Entry type: FAQ Entry ID: 38051505, Entry date: 2024-03-27
- What properties, advantages and special features does the S7 protocol offer?, Entry type: FAQ Entry ID: 26483647, Entry date: 2019-11-26
- What differences are there when configuring S7 connections?, Entry type: FAQ Entry ID: 17991275, Entry date: 2019-11-26
Histórico
| Data | Descrição |
|---|---|
| 2025-10-18 | First version. |